Water Stratification Article

Water stratification influenced the distribution and dynamics of anammox bacteria in a subtropical stratified reservoir xue et al 2017.
Water stratification article. Temperature stratification in water heaters means that water is not evenly warm throughout the vessel but rather arranged in layers of cold warm water given the different density of cold and hot water. In fact sunlight often only penetrates a few metres into the lake directly warming just the top few metres. Stratification in water heaters offers legionella bacteria ideal temperatures for growth 20 45 c. These layers are normally arranged according to density with the least dense water masses sitting above the more dense layers.
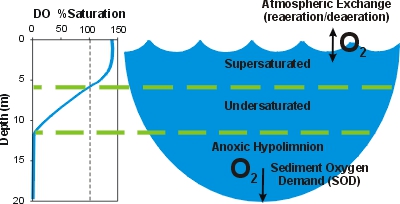
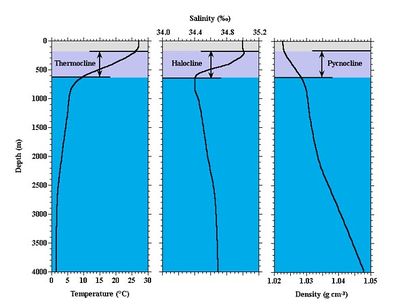
However to date few studies have reported the effects of reservoir water stratification and mixing on the aquatic microbial composition functional community evolution and relative influence of environmental driving factors in stratified drinking water reservoirs. When the ice has melted in the spring solar radiation warms the water at the surface of the lake much faster than in deeper waters. Why is stratification in water heaters a problem. Water stratification is when water masses with different properties salinity halocline oxygenation chemocline density pycnocline temperature thermocline form layers that act as barriers to water mixing which could lead to anoxia or euxinia.
In bodies of fresh water the temperature of the water of greatest density is 4 c and the stratification depends solely on temperature. Stratification is more likely when the mixing forces of wind and wave action are minimal and this occurs more often in the summer months. Thermal stratification occurs when the water in a lake forms distinct layers through heating from the sun. In oceans and seas stratification is governed mainly by variations in water temperature and salinity at the surface and also below the surface where the variations are due to advection and adiabatic processes.




















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/stratified-epithelium/kxsJZMc6RS4j61ethfEOw_A4WBRjTb2LJJRtmn2wVxCw_stratified_squamous_epithelia02.png)






