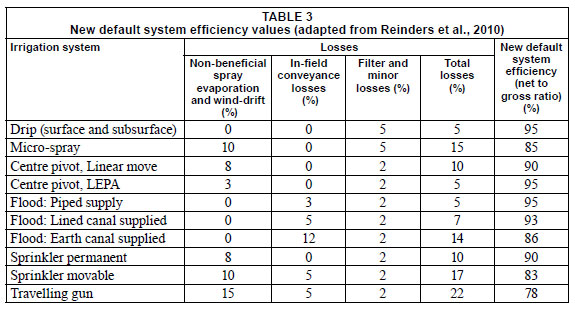
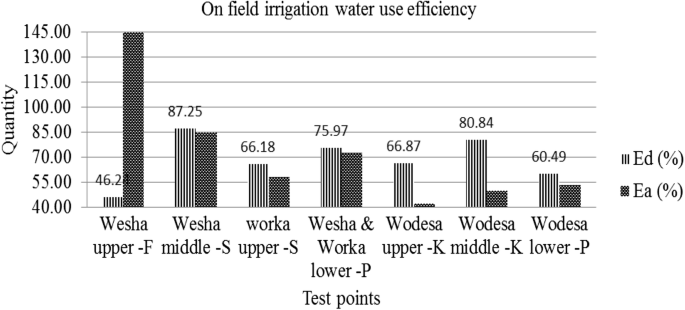
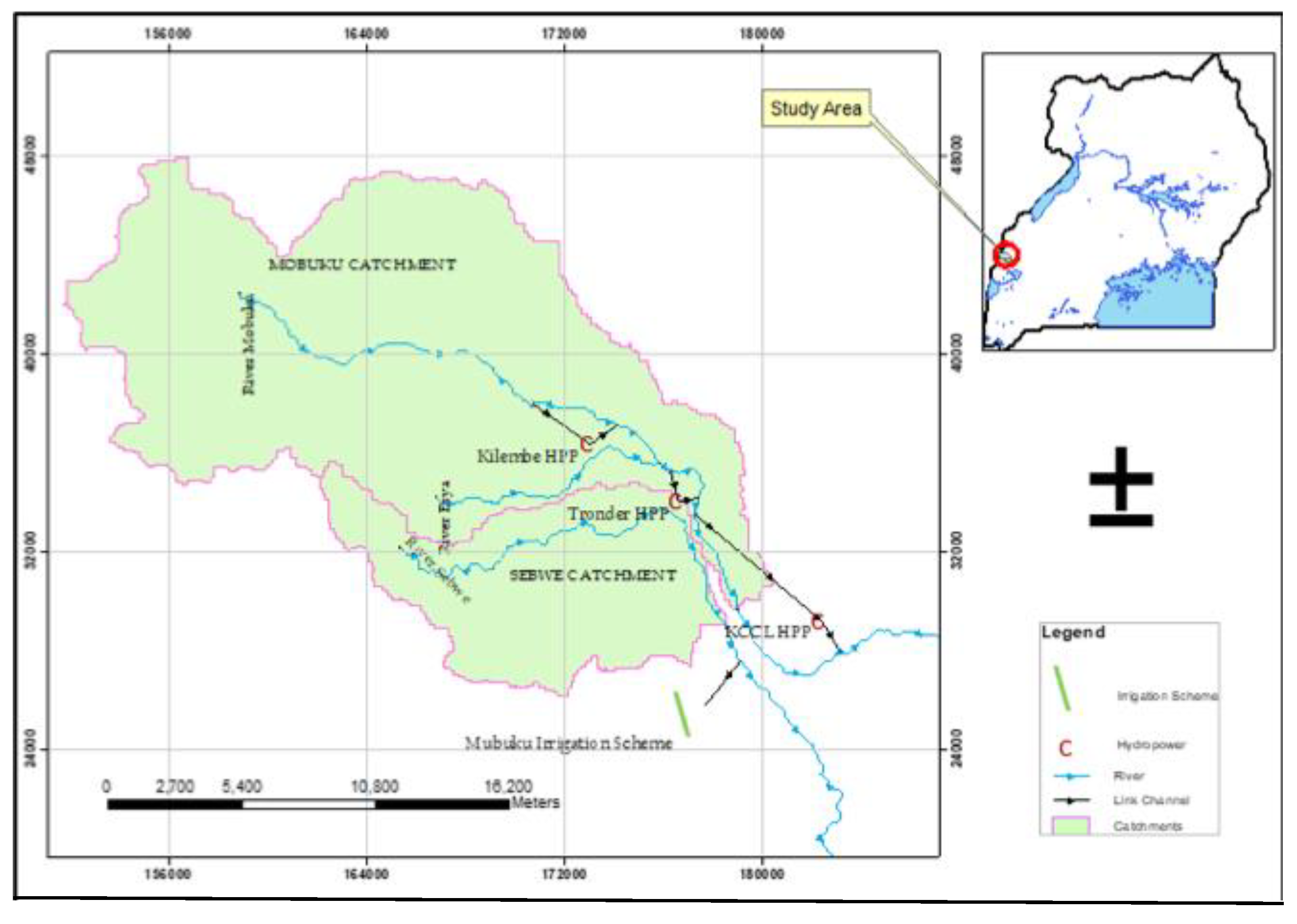
Water Conveyance Efficiency

Water efficient solutions residential.
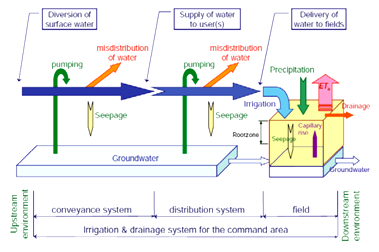
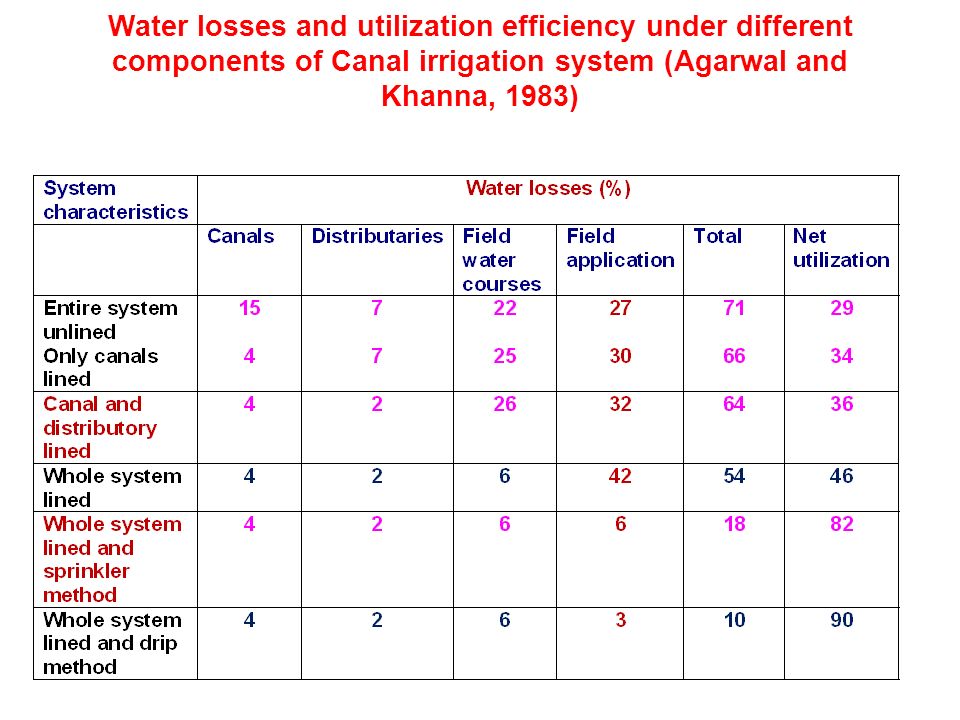
Water conveyance efficiency. The conveyance efficiency normally dictates the amount of water to be delivered to the field which depends on the characteristics of the channel. Water conveyance efficiency is the ratio of the volume of water delivered for irrigation to the volume of water placed in the conveyance system. It is also used to measure the efficiency of channels conveying water from wells and ponds to fields. Conveyance loss reductions were stable at about 50 million m sup 3 sup so 70 to 75 of the potential water savings were achieved through reduced on farm demand.
It is the ratio of the water stored in root zone of plants to the water applied. Turning off the tap while brushing teeth a running tap can waste over six liters per minute. Mean seasonal naturalized flows available for use in southern alberta from 1912 to 2009 ranged from 2 08 billion m sup 3 sup in high demand years to 3 95 billion m sup 3 sup in wet years. This ratio is normally less than 1 0 for open channel conveyance systems but it may be approximately 1 0 for pipeline conveyance systems.
It is the ratio of the amount of water applied to the land to the amount of. Water conveyance efficiency may be defined as the percentage ratio of the amount of water delivered to fields or farms to the amount of water diverted from sources. Conveyance efficiency is used to evaluate the efficiency of the system conveying water. Identifying and eliminating wastage such as leaks and inefficient processes such as continual spray.
Types of irrigation efficiency a water conveyance efficiency ηc. Water conveyance efficiency definition english. Ratio of the volume of irrigation water delivered by a distribution system to the water introduced into the system. The conveyance efficiency will decrease as a result of water losses including canal seepage canal spills evaporation from canals and leaks in pipelines.
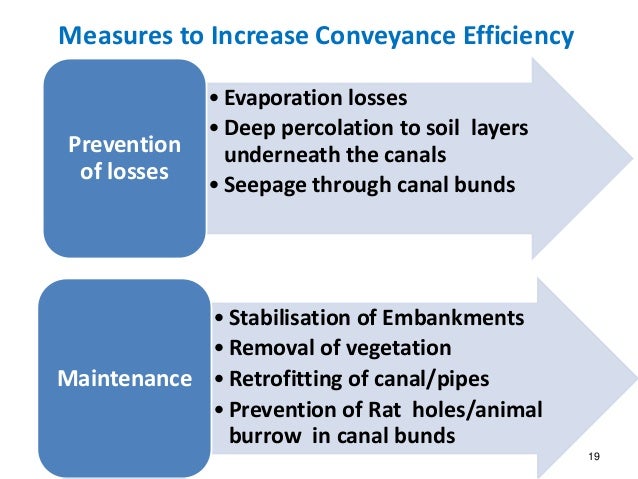
In the process of transporting water from the source to the farm land there is water loss through evaporation transpiration percolation and spills.